All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
Interact these issues to relevant job teams, follow up up until there's a remedy, and report the client resolution. Make certain that all tasks are following their budget plans and distribution times. Make a routine of tracking project milestones and dependencies. Consist of these things in your regular reports. Collaborate with other appropriate departments, including the product, sales, and support divisions.
Develop a system to strategy, track, and record every program you take care of. Provide regular feedback to core groups, including the item group, engineering group, and development group. A bachelor's degree in computer system science or an associated field is necessary. A minimum of 4-6 years of experience in program management with IT tasks is critical.
Technology is nitty-gritty when it concerns the innovation sector, and within that paradigm, there's a behind-the-scenes orchestrator guaranteeing whatever runs seamlesslythe Technical Program Supervisor (TPM). This unsung hero plays a crucial function in the success of tech tasks, bringing order to mayhem and ensuring that the gears of development turn smoothly.
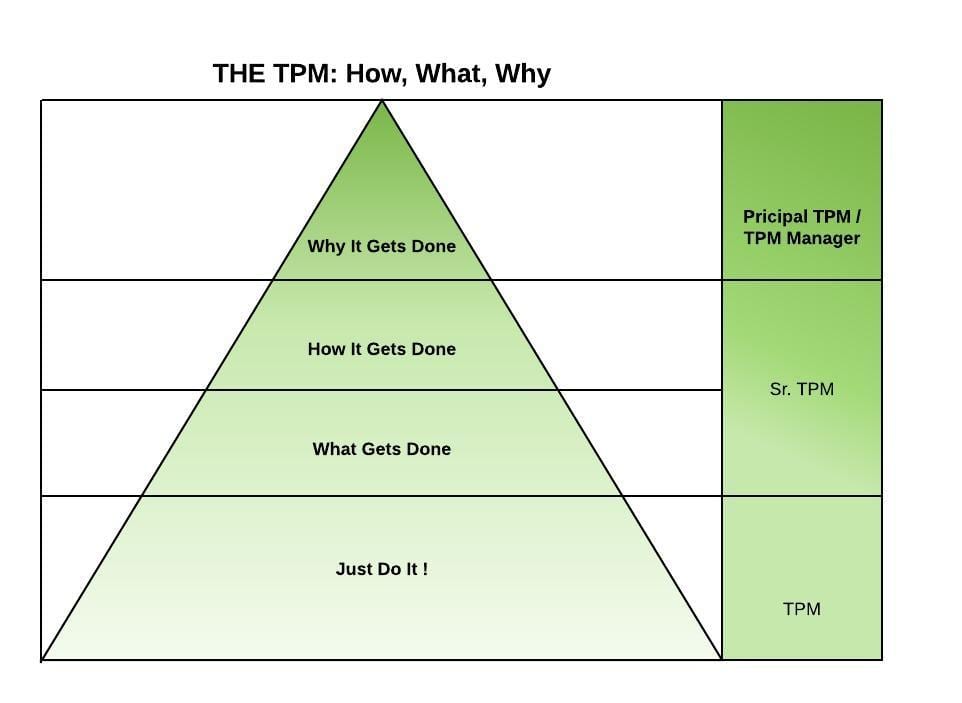
Technical Program Management Career Path
It's a fragile dance between establishing ambitious goals and making sure expectations stay strongly based in reality - how to become a tpm. technical program manager certification. It's not just about producing a strategy; it's regarding performing it perfectly. TPMs put on the hats of both visionary coordinators and pragmatic executors, making certain that every action lines up with the overarching job objectives

In the substantial landscape of tech tasks, effective interaction is the bridge that links disparate teams and stakeholders. Here, TPMs beam as experienced translators, deciphering the complex language of technology for non-technical stakeholders. They bridge the space, guaranteeing that every person, regardless of their technical background, understands the project's objectives and development.
They have the foresight to identify possible risks, ranging from unpredicted technical difficulties to external aspects past the team's control. TPMs establish methods to alleviate threats, ensuring that the project cruises through rainy climate with strength.
Right here, TPMs take on the function of allocators-in-chief, strategically dispersing sources to optimize effectiveness. As the job landscape changes, TPMs reallocate sources dynamically, guaranteeing that the group continues to be agile and responsive.
Tpm Roadmap
TPMs, in this respect, become the gatekeepers of quality. They established stringent requirements for every element of the job, from code to style, ensuring that the end product fulfills or surpasses the defined criteria.
TPMs develop a society where excellence is not just a goal yet a practice, permeating every element of the task. Via their thorough oversight, they impart confidence in stakeholders and contribute to the long-lasting success and reputation of the organization. Being an effective TPM needs even more than simply a flair for job management.
Why should I pursue a career as a Tpm Salary Expectations?
While TPMs might not be coding wizards, they need a solid understanding of the technical landscape. This consists of experience with the innovations entailed, an awareness of market patterns, and the ability to understand the effects of technological decisions.
TPMs are the interaction nexus of a task. Whether it's communicating intricate technological details to a non-technical audience or promoting cooperation amongst group members, efficient interaction is non-negotiable.
As modern technology evolves, so does the role of the TPM. Agile has come to be a lot more than simply a buzzword; it's a means of life for lots of TPMs.
, has actually become a foundation in the TPM's toolkit. In the age of large data, TPMs are increasingly counting on data-driven understandings to notify their decision-making procedures.
What does the career path look like for a Program Management Certification For Tech?

Unlike traditional project managers, TPMs need to deeply comprehend the technological aspects of the tasks they take care of. This dual know-how permits them to communicate with design groups efficiently, understand technological difficulties, and ensure that tasks are finished in a timely manner and within spending plan. Whether you're wanting to hire a TPM or turn into one, recognizing the responsibilities and skill sets required is vital for success in the technology sector.
The courses cover necessary topics such as project lifecycle monitoring, danger analysis, resource allowance, and software application growth procedures. With a focus on real-world applications, our training guarantees you are prepared to deal with the complexities of technical tasks in any market. Making a qualification can substantially boost your career prospects, showing to companies that you possess the expertise and skills required to succeed in a TPM function.
From startups to Ton of money 500 firms, companies around the world are looking for certified specialists to lead their technical programs. Whether you're aiming to hire a TPM or want TPM tasks, TPM Institute can aid you navigate the work market and attach you with the appropriate chances. Our courses are not almost discovering; they are concerning launching your job in among one of the most in-demand areas in the tech market.
Our are committed to supplying you with the very best feasible education, offering insights based in real-world experience. They are devoted to assisting you attain your accreditation and succeed in your profession. To learn more regarding our programs and qualifications, at Take the next action in your profession with TPM Institute and end up being a leader in technical program management.
Microsoft Technical Program Manager Interview
There's a propensity for individuals to move towards extremes when conceptualizing technical program supervisors. As an example, they're typically explained as either constantly participating in coding or otherwise at all. The reality exists is a range of technical deepness amongst TPMs, and this usually differs by project and client. Some jobs need a leader with simply adequate technological deepness to comprehend innovation style and compromises.
They can articulate intricate technical principles to non-technical stakeholders and assist in collaboration between varied groups. TPMs stand out at identifying and fixing problems that emerge throughout project execution, making certain that tasks remain on timetable and within spending plan.
TPMs work to guarantee that all group participants are functioning towards the exact same goals, protecting against miscommunication and thrown away effort. They expect and adapt to changes in task needs, making sure that projects can pivot efficiently when needed. TPMs proactively attend to possible problems, lowering the chance of project hold-ups and failures. They urge their groups to explore originalities and technologies, driving continual renovation and growth.
TPMs function to make certain that all group participants are functioning in the direction of the same purposes, preventing miscommunication and wasted initiative. TPMs proactively attend to prospective issues, lowering the possibility of job hold-ups and failures.
Latest Posts
How To Prepare For A Software Engineering Whiteboard Interview
How To Ace A Live Coding Technical Interview – A Complete Guide
Netflix Software Engineer Interview Guide – Insider Advice